Understanding the Function and Disorders of the Cochlear Nerve
The cochlear nerve plays a crucial role in our ability to hear and interpret sound. Located within the inner ear, this nerve is responsible for transmitting auditory information from the cochlea to the brain. In this article, we will delve into the anatomy and function of the cochlear nerve, explore common disorders associated with it, discuss available treatment options, and highlight the impact of cochlear nerve disorders on quality of life.
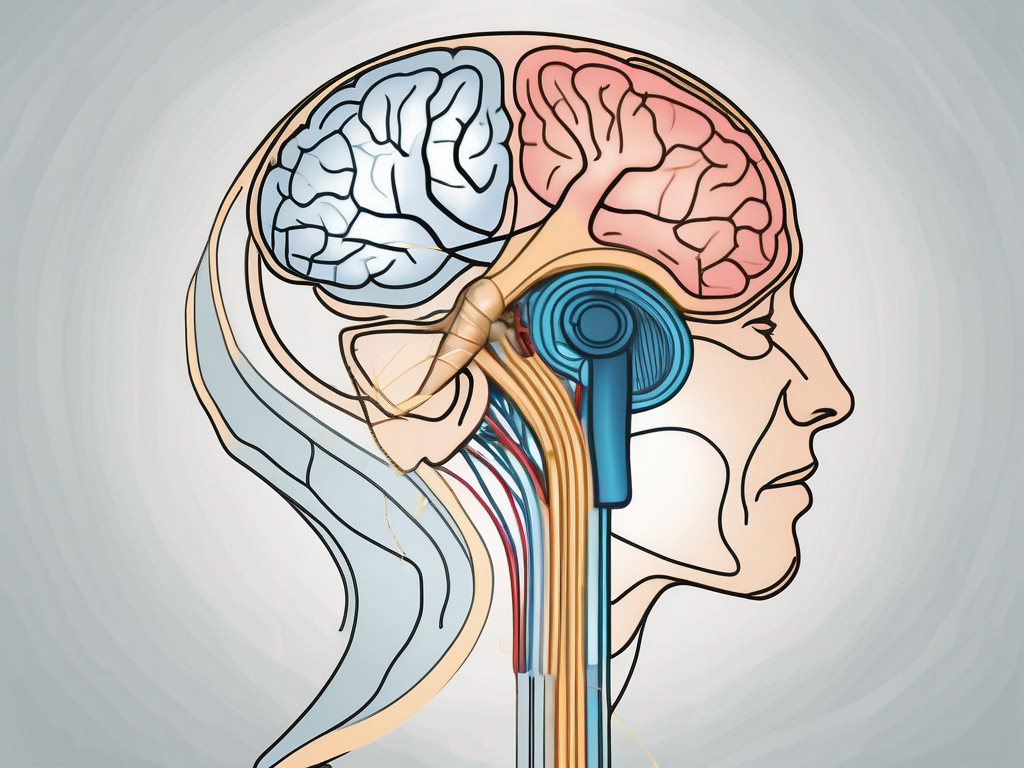
Anatomy of the Cochlear Nerve
The cochlear nerve is a bundle of nerve fibers that originates in the cochlea, a spiral-shaped structure within the inner ear. It consists of two main components: the vestibular nerve and the cochlear nerve proper. While the vestibular nerve is responsible for transmitting information related to balance and spatial orientation, the cochlear nerve proper is dedicated to relaying auditory signals. These signals are then processed in the brain, allowing us to perceive sound.
The cochlear nerve is a fascinating part of the auditory system. It is a complex network of nerve fibers that work together to transmit sound information from the cochlea to the brain. These nerve fibers are incredibly delicate and sensitive, allowing for the precise transmission of electrical signals that ultimately result in our ability to hear and comprehend the world around us.
The Role of the Cochlear Nerve in Hearing
When sound enters the ear, it causes vibrations in the fluid-filled cochlea. These vibrations are picked up by tiny sensory hair cells, which convert them into electrical signals. The cochlear nerve then carries these signals to the brain, where they are interpreted as sound. This intricate process illustrates the crucial role played by the cochlear nerve in our ability to hear and comprehend the world around us.
Imagine a symphony orchestra playing a beautiful piece of music. As the musicians play their instruments, the sound waves travel through the air and enter your ear. These sound waves then travel through the ear canal and reach the cochlea, where the magic begins. The cochlear nerve acts as the conductor, carefully orchestrating the transmission of these sound signals to the brain. It ensures that every note, every melody, and every rhythm is accurately conveyed, allowing us to fully experience the beauty of music.
The Pathway of Sound: From Ear to Brain
Understanding the pathway through which sound travels from the ear to the brain is essential in comprehending the function of the cochlear nerve. After being collected by the cochlea, the electrical signals generated by the sensory hair cells travel along the cochlear nerve and enter the brainstem. From there, they are relayed to the auditory cortex, where they are processed and interpreted as distinct sounds. Any disruption along this pathway can result in hearing impairment or loss.
Think of the pathway of sound as a well-organized highway system. The cochlear nerve acts as the main road, efficiently carrying the electrical signals from the cochlea to the brain. Along this highway, there are various checkpoints and intersections where the signals are carefully monitored and directed. These checkpoints ensure that the signals reach their intended destination in the auditory cortex, where they can be transformed into the beautiful symphony of sounds that we perceive.
It is truly remarkable how the cochlear nerve, with its intricate network of nerve fibers, allows us to experience the richness and diversity of the auditory world. From the delicate sound of a whisper to the thunderous roar of a waterfall, the cochlear nerve faithfully carries these auditory signals, painting a vivid picture of the world around us.
Common Disorders of the Cochlear Nerve
Despite the crucial role it plays, the cochlear nerve is susceptible to various disorders that can affect our hearing abilities. These disorders may arise from a variety of factors, including genetic predisposition, exposure to loud noises, infections, or certain medications. It is important to be aware of the symptoms associated with these disorders in order to seek necessary medical assistance.
The cochlear nerve, also known as the auditory nerve, is a vital component of our auditory system. It is responsible for transmitting sound signals from the cochlea to the brain, allowing us to perceive and interpret sounds. However, this intricate network of nerve fibers can be disrupted by a range of disorders, leading to hearing impairments and other related symptoms.
One common disorder of the cochlear nerve is sensorineural hearing loss. This condition occurs when there is damage to the hair cells or nerve fibers within the cochlea or along the cochlear nerve pathway. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetic mutations, aging, exposure to loud noises, or certain medical conditions.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Cochlear Nerve Disorders
Individuals experiencing cochlear nerve disorders may notice symptoms such as hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), dizziness, or problems with balance. These symptoms can vary in severity and may have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
During a medical evaluation, the healthcare professional will conduct a thorough examination of your ears and may perform tests such as audiograms or imaging studies to assess the health of the cochlear nerve. Audiograms are tests that measure your ability to hear different tones and pitches, while imaging studies, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), can provide detailed images of the cochlea and the surrounding structures.
By diagnosing the specific disorder affecting the cochlear nerve, healthcare professionals can develop an appropriate treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs. Treatment options may include hearing aids, cochlear implants, medication, or surgical interventions, depending on the underlying cause and severity of the disorder.
Genetic and Environmental Factors in Cochlear Nerve Disorders
Research has shown that both genetic and environmental factors can contribute to the development of cochlear nerve disorders. Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to these disorders, meaning they have inherited certain gene mutations that increase their susceptibility. These genetic mutations can affect the structure or function of the cochlea or the cochlear nerve, leading to hearing impairments.
On the other hand, environmental factors can also play a significant role in the development of cochlear nerve disorders. Exposure to loud noises, such as prolonged or intense noise from machinery, concerts, or firearms, can damage the delicate hair cells within the cochlea and disrupt the transmission of sound signals along the cochlear nerve pathway. Certain medications, such as certain antibiotics or chemotherapy drugs, may also have ototoxic effects, causing damage to the cochlea and resulting in hearing loss.
Infections, particularly bacterial or viral infections, can also affect the cochlear nerve. Meningitis, for example, is an infection that can cause inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. If the infection spreads to the cochlea or the cochlear nerve, it can lead to hearing loss or other auditory complications.
Understanding these risk factors can help identify individuals who may be more susceptible to developing cochlear nerve disorders and guide preventative measures. For example, individuals with a family history of hearing loss or known genetic mutations associated with cochlear nerve disorders may benefit from regular hearing screenings and protective measures, such as avoiding excessive noise exposure and using ear protection in noisy environments.
In conclusion, the cochlear nerve is vulnerable to various disorders that can impair our hearing abilities. These disorders can arise from genetic predisposition, exposure to loud noises, infections, or certain medications. Recognizing the symptoms, seeking timely medical assistance, and understanding the underlying genetic and environmental factors can help in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of cochlear nerve disorders.
Treatment Options for Cochlear Nerve Disorders
When it comes to treating cochlear nerve disorders, it is important to note that each case is unique. Treatment options can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the disorder. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to determine the most suitable course of action.
Cochlear nerve disorders can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life. The ability to hear and communicate effectively is essential for social interactions, work, and overall well-being. Therefore, exploring various treatment options is crucial in order to address the specific needs of each patient.
Medication and Therapy for Cochlear Nerve Disorders
In some cases, medication or therapy may be employed to manage symptoms associated with cochlear nerve disorders. Medications, such as corticosteroids, may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms such as hearing loss or tinnitus. These medications work by suppressing the immune response and reducing the swelling of the cochlear nerve, which can help improve auditory function.
Furthermore, therapy techniques, such as auditory rehabilitation or hearing aids, can play a vital role in the treatment of cochlear nerve disorders. Auditory rehabilitation focuses on improving communication skills and maximizing the use of residual hearing. This can involve speech therapy, auditory training, and counseling to help individuals adapt to changes in their hearing abilities. Hearing aids, on the other hand, are electronic devices that amplify sound and make it easier for individuals with hearing loss to perceive and understand speech and other sounds.
Surgical Interventions for Cochlear Nerve Disorders
In more severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to address cochlear nerve disorders. Procedures such as cochlear implants or auditory brainstem implants can be considered for individuals who have significant hearing loss or are unable to benefit from other treatment options.
Cochlear implants are electronic devices that bypass the damaged or non-functioning parts of the cochlear nerve and directly stimulate the auditory nerve. They consist of an external component, which captures sound and converts it into electrical signals, and an internal component, which is surgically implanted under the skin and delivers the signals to the auditory nerve. Cochlear implants can provide a sense of sound to individuals who are profoundly deaf or have severe hearing loss.
Auditory brainstem implants, on the other hand, are designed for individuals who have no functioning cochlear nerve. This can occur in cases where the cochlear nerve is absent or damaged beyond repair. Auditory brainstem implants work by directly stimulating the brainstem, bypassing the cochlear nerve altogether. This surgical intervention can help individuals with auditory nerve disorders regain some level of hearing and improve their ability to understand speech and environmental sounds.
In conclusion, the treatment options for cochlear nerve disorders are diverse and depend on the specific needs of each individual. Medication and therapy can be effective in managing symptoms and improving quality of life, while surgical interventions such as cochlear implants or auditory brainstem implants may be necessary for more severe cases. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial in order to determine the most appropriate treatment plan and achieve the best possible outcomes for individuals with cochlear nerve disorders.
The Impact of Cochlear Nerve Disorders on Quality of Life
Living with cochlear nerve disorders can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Hearing loss, in particular, can result in communication difficulties, social isolation, and psychological effects. It is crucial to acknowledge the emotional and psychological aspects associated with these disorders and offer support and coping strategies to affected individuals.
When an individual experiences hearing loss due to cochlear nerve disorders, their ability to communicate effectively may be compromised. Simple tasks, such as having a conversation or participating in group activities, can become challenging and frustrating. The inability to hear and understand others can lead to feelings of isolation and exclusion.
Moreover, the psychological effects of hearing loss can be profound. The constant struggle to hear and comprehend sounds can cause feelings of frustration and irritability. Individuals may also experience anxiety in social situations, fearing that they will not be able to fully participate or understand what is being said. These psychological challenges can take a toll on an individual’s self-esteem and overall well-being.
The Psychological Effects of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can have far-reaching psychological effects, impacting an individual’s self-esteem, relationships, and overall well-being. It may lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, and depression. Recognizing these emotional challenges is essential in providing comprehensive care and support for individuals with cochlear nerve disorders.
Individuals with cochlear nerve disorders may struggle with self-esteem issues due to their hearing loss. They may feel self-conscious about their inability to hear and worry about how others perceive them. These feelings can lead to a loss of confidence and a reluctance to engage in social activities.
Furthermore, relationships can be affected by hearing loss. Communication is a fundamental aspect of any relationship, and when one person has difficulty hearing, it can strain their interactions with loved ones. Misunderstandings and miscommunications can occur, leading to frustration and tension in relationships.
Additionally, the psychological effects of hearing loss can extend beyond personal relationships. In professional settings, individuals may face challenges in their careers due to difficulties in communication. This can result in decreased job satisfaction and opportunities for advancement.
Coping Strategies and Support for Individuals with Cochlear Nerve Disorders
Fortunately, there are numerous coping strategies and support systems available to help individuals with cochlear nerve disorders navigate the challenges they may face. Communication techniques, such as lip-reading or sign language, can enhance communication abilities. These techniques can empower individuals to actively participate in conversations and maintain meaningful connections with others.
Joining support groups specifically designed for individuals with cochlear nerve disorders can also provide a valuable source of emotional support and encouragement. These groups offer a safe space for individuals to share their experiences, exchange coping strategies, and learn from others who have faced similar challenges. The sense of community and understanding can help alleviate feelings of isolation and provide a network of support.
In addition to support groups, seeking counseling services can be beneficial for individuals with cochlear nerve disorders. Professional counselors can provide guidance and help individuals navigate the emotional challenges associated with hearing loss. They can offer coping strategies, teach stress management techniques, and assist in developing a positive mindset.
Furthermore, technological advancements have made significant contributions to improving the quality of life for individuals with cochlear nerve disorders. Cochlear implants and hearing aids are two examples of assistive devices that can enhance an individual’s ability to hear and communicate effectively. These devices can provide a sense of normalcy and improve overall well-being.
In conclusion, living with cochlear nerve disorders, particularly hearing loss, can have a profound impact on an individual’s quality of life. The psychological effects, such as decreased self-esteem and strained relationships, can further exacerbate the challenges faced by individuals with these disorders. However, through the utilization of coping strategies, support systems, and assistive devices, individuals can navigate these challenges and lead fulfilling lives. It is essential for healthcare professionals and society as a whole to recognize the significance of these disorders and provide the necessary support and resources to improve the quality of life for affected individuals.
Future Research Directions in Cochlear Nerve Health
Advances in medical research continue to shed light on the complexities of cochlear nerve disorders, paving the way for novel treatment modalities and potential avenues for regeneration.
Advances in Cochlear Nerve Disorder Treatment
Ongoing research efforts are focused on developing more targeted and effective treatment options for cochlear nerve disorders. This includes investigating the use of regenerative therapies, such as stem cell transplantation or gene therapy, to repair damaged or non-functioning parts of the cochlear nerve. These advancements hold great promise for individuals affected by these disorders.
The Promise of Stem Cell Research in Cochlear Nerve Regeneration
Stem cell research has emerged as a promising field in the context of cochlear nerve regeneration. Scientists are exploring the potential of utilizing stem cells to regenerate damaged sensory hair cells or even the cochlear nerve itself. While this research is still in its early stages, it offers hope for future breakthroughs in the treatment of cochlear nerve disorders.
In conclusion, understanding the function and disorders of the cochlear nerve is crucial in appreciating the intricate processes involved in our ability to hear. By exploring the anatomy, function, and common disorders associated with the cochlear nerve, as well as available treatment options and the impact of these disorders on quality of life, we can enhance our knowledge and promote a greater understanding of the challenges faced by individuals affected by cochlear nerve disorders.