The cochlear nerve is a crucial component of our auditory system, responsible for transmitting sound signals from the inner ear to the brain. When this nerve is affected by a lesion or damage, it can have profound effects on our hearing and overall well-being. In this article, we will explore the anatomy and function of the cochlear nerve, the impact of lesions on this nerve, the side effects that can arise, and the available treatment and management options. We will also delve into the prevention and risk factors associated with cochlear nerve lesions.
Understanding the Cochlear Nerve and Its Function
Anatomy of the Cochlear Nerve
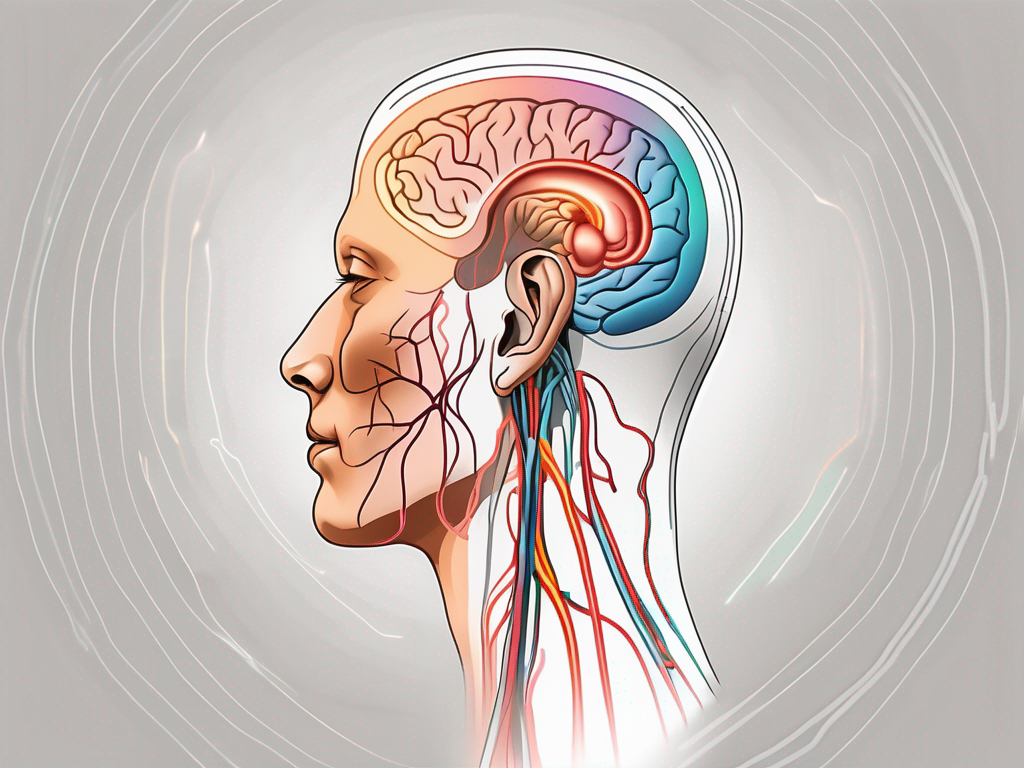
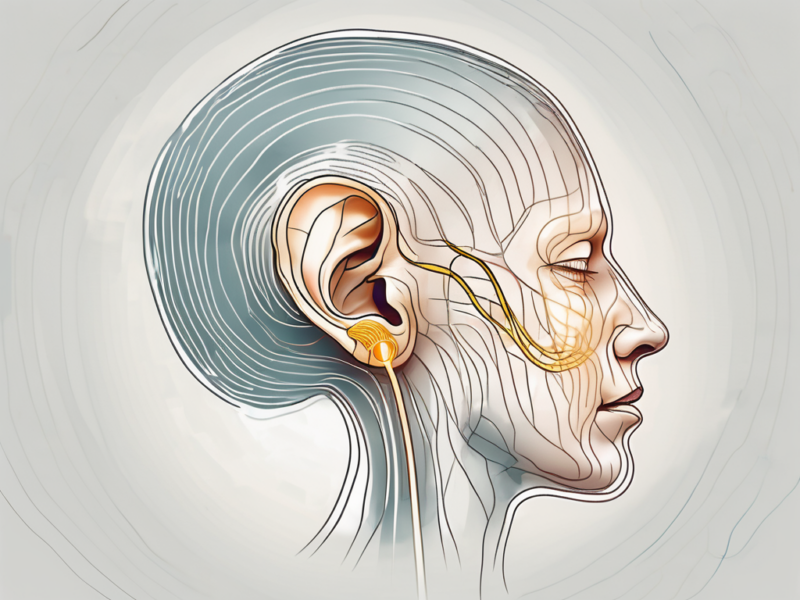
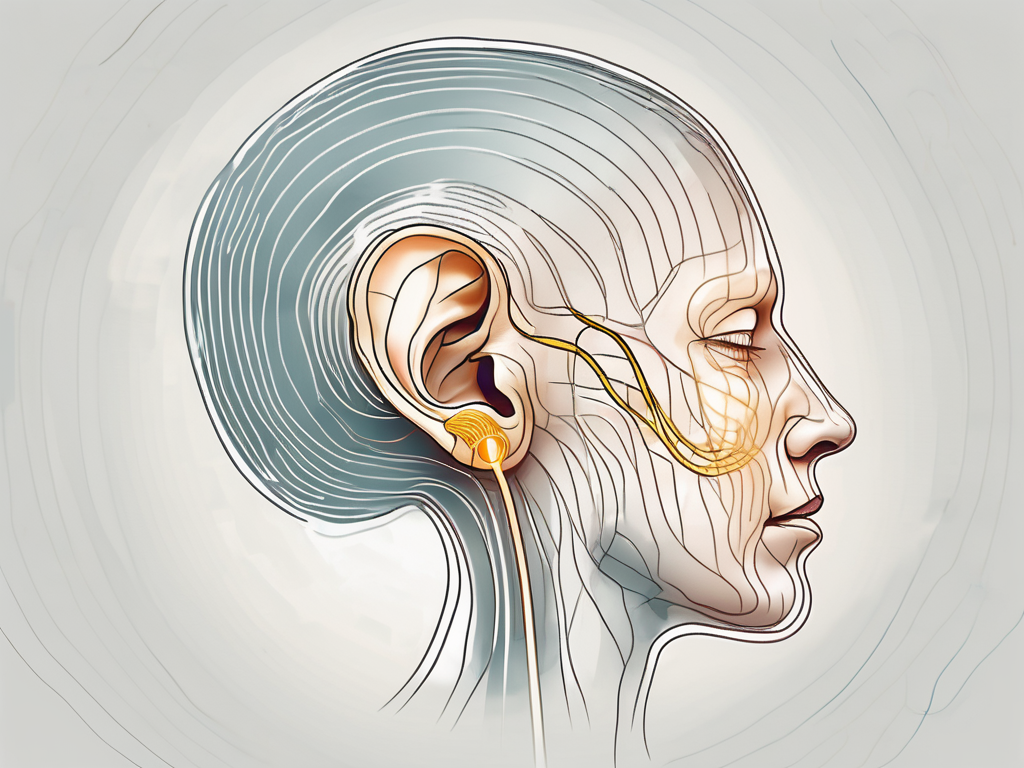
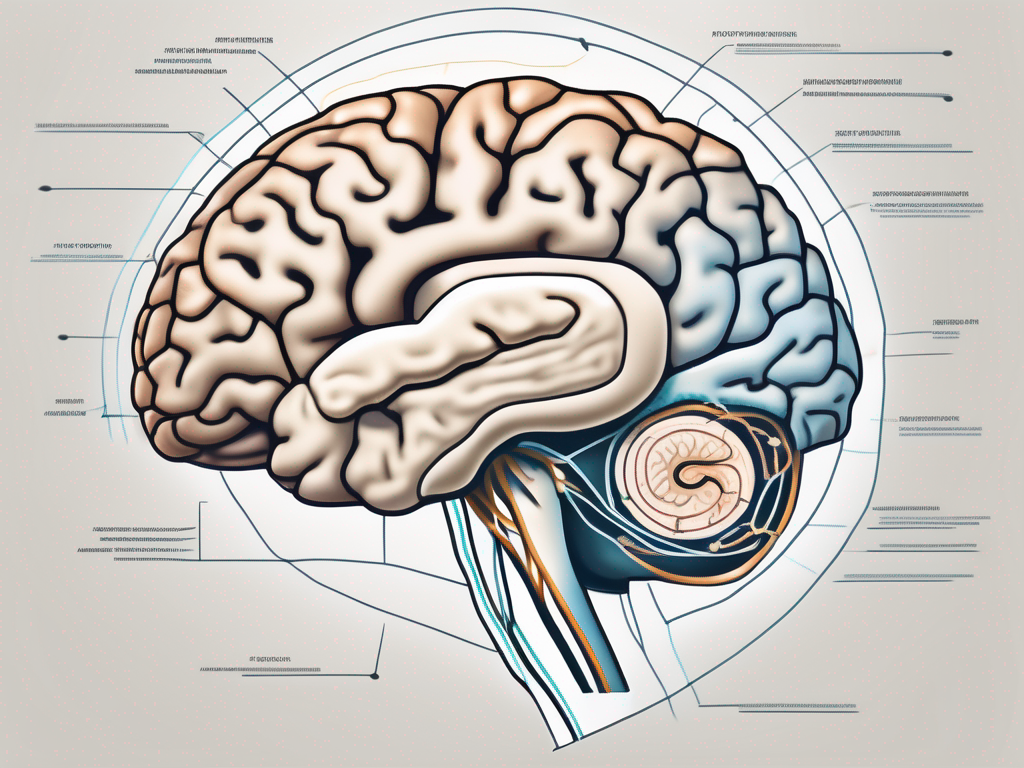
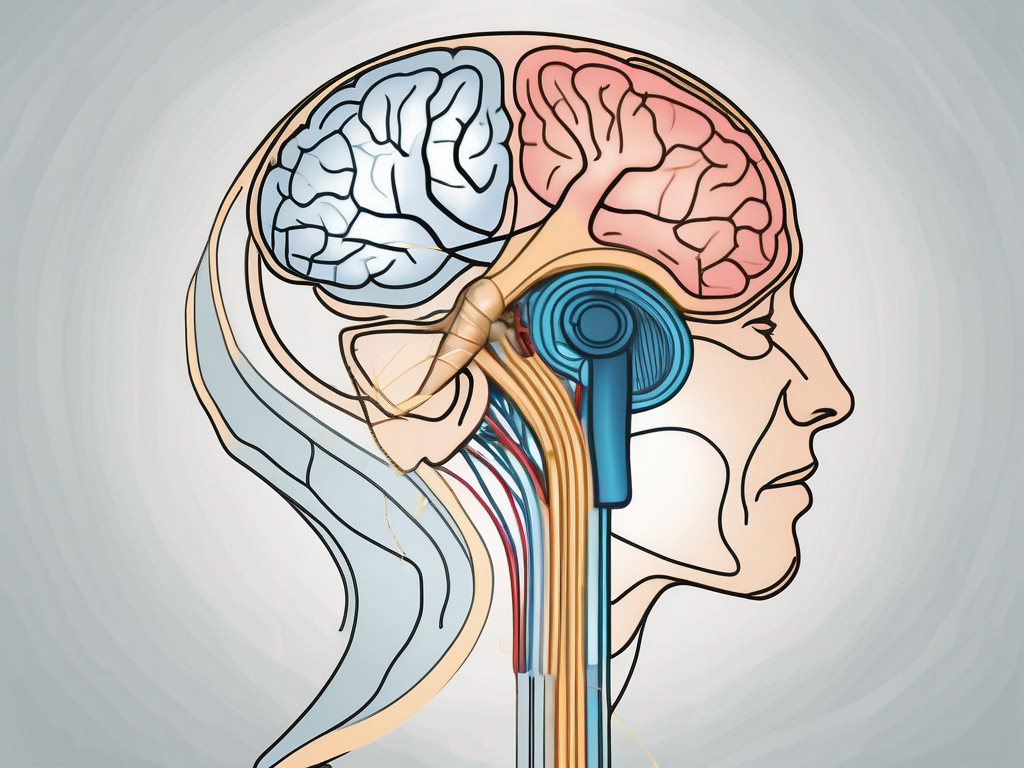
The cochlear nerve is a branch of the vestibulocochlear nerve, also known as the eighth cranial nerve. It is a paired nerve that connects the cochlea, the spiral-shaped structure in the inner ear, to the brainstem. The cochlear nerve carries the sensory information of sound from the cochlea to the brain, allowing us to perceive and interpret sounds.
The cochlear nerve is a fascinating component of the auditory system. It consists of thousands of individual nerve fibers that are responsible for transmitting auditory signals from the cochlea to the brain. These fibers are incredibly delicate and precise, ensuring that the information they carry is accurately relayed to the brain for processing.
The cochlear nerve is intricately connected to the cochlea, which plays a crucial role in the process of hearing. The cochlea is a remarkable structure that resembles a snail shell and is filled with fluid. Within the cochlea, there are specialized cells called hair cells that are responsible for converting sound waves into electrical signals.
Role of the Cochlear Nerve in Hearing
As sound waves enter the ear, they cause vibrations in the cochlea, which in turn stimulate the hair cells lining the inner walls of the cochlea. These hair cells convert the mechanical vibrations into electrical signals, which are then transmitted by the cochlear nerve to the brain. The brain processes these electrical signals into the sounds we perceive, enabling us to understand and communicate with the world around us.
The cochlear nerve acts as a vital link between the cochlea and the brain. Without this nerve, the auditory information gathered by the hair cells would remain trapped within the cochlea, rendering us unable to hear and comprehend sounds. The cochlear nerve’s ability to transmit electrical signals with remarkable precision allows us to experience the richness and complexity of the auditory world.
It is important to note that the cochlear nerve is not solely responsible for hearing. It works in conjunction with other components of the auditory system, such as the brainstem and the auditory cortex, to process and interpret sound. The cochlear nerve acts as the messenger, delivering the auditory information to the brain for further analysis and understanding.
Furthermore, the cochlear nerve is not only involved in the perception of sound but also plays a role in maintaining balance. As part of the vestibulocochlear nerve, it carries information related to the body’s position and movement, contributing to our overall sense of equilibrium.
In conclusion, the cochlear nerve is a remarkable structure that plays a crucial role in our ability to hear and understand the world around us. Its intricate connection to the cochlea and its precise transmission of electrical signals to the brain allow us to experience the beauty of sound and maintain our sense of balance. Understanding the function of the cochlear nerve provides us with a deeper appreciation for the complexity and wonder of the human auditory system.
Impact of Lesions on the Cochlear Nerve
The cochlear nerve plays a crucial role in transmitting auditory information from the inner ear to the brain. When this nerve is affected by lesions or damage, it can have a profound impact on an individual’s ability to hear and process sound. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and diagnosis of cochlear nerve lesions is essential for effective management and treatment.
Causes of Cochlear Nerve Lesions
There are various factors that can lead to lesions or damage in the cochlear nerve. One common cause is prolonged exposure to loud noises. Continuous exposure to high decibel levels can gradually wear down the delicate structures of the inner ear, including the cochlear nerve. This can result in permanent hearing loss or other auditory impairments.
Head trauma is another significant cause of cochlear nerve lesions. A severe blow to the head can damage the nerve fibers, disrupting the transmission of auditory signals. This can lead to a range of hearing problems, depending on the extent and location of the injury.
Tumors can also affect the cochlear nerve. Both benign and malignant growths can put pressure on the nerve, interfering with its normal function. In some cases, surgical removal of the tumor may be necessary to alleviate the symptoms and prevent further damage.
Infections, such as meningitis or labyrinthitis, can cause inflammation and damage to the cochlear nerve. These infections can be bacterial or viral in nature and often require prompt medical intervention to prevent long-term complications.
Certain medications, such as ototoxic drugs, have the potential to cause cochlear nerve lesions. These drugs can have a toxic effect on the nerve fibers, leading to hearing loss or other auditory problems. It is crucial for healthcare providers to carefully consider the potential risks and benefits of these medications before prescribing them.
It is important to note that the causes of cochlear nerve lesions can vary from person to person. Some individuals may be more susceptible to certain factors, while others may have a genetic predisposition to developing nerve damage. Consulting with a medical professional is essential for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Cochlear Nerve Lesions
When the cochlear nerve is affected, individuals may experience a range of symptoms that can significantly impact their quality of life. One of the most common symptoms is hearing loss. Depending on the severity and location of the lesions, the hearing loss can range from mild to profound, making it difficult to understand speech or perceive certain sounds.
Tinnitus, or ringing in the ears, is another prevalent symptom of cochlear nerve lesions. The phantom sounds can vary in intensity and pitch, causing distress and interfering with daily activities. Managing tinnitus often requires a multidisciplinary approach, including counseling, sound therapy, and sometimes medication.
Dizziness and difficulties with balance are also common symptoms associated with cochlear nerve lesions. The inner ear plays a crucial role in maintaining balance, and when the nerve is damaged, it can lead to vertigo, unsteadiness, and a higher risk of falls. Vestibular rehabilitation therapy is often recommended to help individuals regain their balance and reduce dizziness.
Diagnosing cochlear nerve lesions involves a comprehensive evaluation by a medical professional specializing in audiology or otolaryngology. The diagnostic process may include a thorough medical history review, physical examination, hearing tests, and imaging studies, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans. These tests help identify the location and extent of the lesions, guiding the development of an appropriate treatment plan.
In conclusion, cochlear nerve lesions can have a significant impact on an individual’s auditory function and overall well-being. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and diagnosis of these lesions is crucial for effective management and treatment. Seeking timely medical evaluation and intervention is essential to minimize the long-term consequences and improve the quality of life for those affected.
Side Effects of Cochlear Nerve Lesions
The cochlear nerve plays a crucial role in our ability to hear and maintain balance. When this nerve is affected by lesions, it can lead to various side effects that significantly impact an individual’s daily life.
Effects on Hearing and Balance
One of the most noticeable side effects of cochlear nerve lesions is hearing loss. The severity of hearing loss can vary depending on the extent of the lesion and its location. Some individuals may experience mild to moderate hearing loss, while others may suffer from profound hearing impairment.
Imagine waking up one day and finding it difficult to hear the sound of your loved ones’ voices or the melodies of your favorite songs. The world suddenly becomes quieter, and conversations become a challenge. Simple tasks like following instructions or participating in group discussions become overwhelming. The frustration and sense of isolation that come with hearing loss can be emotionally draining.
In addition to hearing loss, lesions on the cochlear nerve can also affect an individual’s balance and coordination, leading to dizziness and difficulties with spatial orientation. Simple activities like walking or standing can become a struggle, as the brain struggles to process signals related to balance and movement. This can significantly impact an individual’s independence and overall quality of life.
Psychological Impact of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can have a profound psychological impact on individuals, affecting their emotional well-being and overall quality of life. Communication difficulties, social isolation, and feelings of frustration or depression are common challenges faced by individuals with cochlear nerve lesions.
Imagine feeling disconnected from the world around you, unable to fully engage in conversations or enjoy social gatherings. The constant strain of trying to understand what others are saying can lead to feelings of anxiety and self-consciousness. The fear of missing out on important information or being unable to participate fully in social interactions can take a toll on one’s mental health.
It is crucial for individuals experiencing these emotional effects to seek support from healthcare professionals and consider interventions that can assist in coping with the changes brought about by hearing loss. Rehabilitation programs, such as auditory training and counseling, can help individuals adapt to their new hearing abilities and regain confidence in their communication skills.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. There are support groups, online communities, and resources available to help you navigate the challenges of living with cochlear nerve lesions. With the right support and interventions, individuals can lead fulfilling lives and overcome the obstacles posed by hearing loss.
Treatment and Management of Cochlear Nerve Lesions
Cochlear nerve lesions can have a significant impact on an individual’s hearing ability and overall quality of life. Fortunately, there are a variety of medical interventions and rehabilitation strategies available to address the effects of these lesions.
Medical Interventions for Cochlear Nerve Lesions
When it comes to treating cochlear nerve lesions, there is no one-size-fits-all approach. The choice of medical intervention depends on several factors, including the severity of the hearing loss and the individual’s specific needs.
Hearing aids are a common and effective solution for individuals with mild to moderate hearing loss caused by cochlear nerve lesions. These devices amplify sounds, making them easier to hear and understand. They come in various styles, including behind-the-ear, in-the-ear, and completely-in-the-canal, allowing individuals to choose the option that best suits their preferences and comfort.
For individuals with more severe hearing loss, cochlear implants may be recommended. Unlike hearing aids, which simply amplify sounds, cochlear implants bypass the damaged cochlear nerve and directly stimulate the auditory nerve. This allows individuals to perceive sound signals and regain some level of hearing.
In rare cases where both the cochlear nerve and the auditory nerve are damaged, auditory brainstem implants may be considered. These implants bypass both nerves and directly stimulate the brainstem, providing individuals with a sense of sound.
It is crucial for individuals with cochlear nerve lesions to consult with an otolaryngologist or audiologist to determine the most suitable treatment plan. These healthcare professionals will conduct thorough evaluations to assess the extent of the hearing loss and recommend the appropriate intervention.
Rehabilitation and Coping Strategies for Patients
While medical interventions can significantly improve hearing ability, they may not fully restore it to normal levels. This is where rehabilitation programs and coping strategies play a vital role in helping individuals adapt to the changes caused by cochlear nerve lesions.
Speech therapy is often a crucial component of rehabilitation programs for individuals with cochlear nerve lesions. These therapy sessions focus on improving speech and language skills, helping individuals communicate more effectively. Speech therapists use various techniques, such as auditory training and speech reading, to enhance speech perception and production.
Auditory training is another essential aspect of rehabilitation for individuals with cochlear nerve lesions. This training aims to improve the brain’s ability to interpret and understand sounds. It involves exercises and activities that help individuals recognize different speech sounds, discriminate between similar sounds, and understand speech in noisy environments.
In addition to speech therapy and auditory training, assistive listening devices can also be beneficial for individuals with cochlear nerve lesions. These devices, such as FM systems and personal amplifiers, help individuals hear more clearly in challenging listening situations, such as classrooms or crowded environments.
Furthermore, joining support groups or seeking counseling can provide emotional support and valuable insights from others who have faced similar challenges. These groups offer a safe space for individuals to share their experiences, exchange coping strategies, and find encouragement.
In conclusion, the treatment and management of cochlear nerve lesions involve a combination of medical interventions and rehabilitation strategies. By working closely with healthcare professionals and participating in rehabilitation programs, individuals with cochlear nerve lesions can improve their hearing ability and enhance their overall quality of life.
Prevention and Risk Factors of Cochlear Nerve Lesions
The cochlear nerve plays a crucial role in our auditory system, transmitting sound signals from the inner ear to the brain. Unfortunately, this delicate nerve can be susceptible to damage, leading to a range of hearing and balance issues. While it may not be possible to prevent all cases of cochlear nerve lesions, identifying high-risk individuals and implementing preventive measures can help reduce the likelihood of such damage.
Identifying High-Risk Individuals
There are certain factors that can increase the risk of developing cochlear nerve lesions. Individuals who work in noisy environments, such as construction sites or factories, are more likely to be exposed to high levels of noise on a regular basis. Similarly, those who engage in loud recreational activities, such as attending concerts or using power tools without hearing protection, are also at an increased risk.
Furthermore, having a family history of hearing loss can predispose individuals to cochlear nerve lesions. Genetic factors can play a significant role in the development of various auditory disorders, including damage to the cochlear nerve.
Regular hearing screenings can be a valuable tool in identifying individuals who may be at risk of developing cochlear nerve lesions. These screenings can help detect any early signs of hearing loss or damage, allowing for timely intervention and management.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Modifications
Implementing preventive measures to protect the cochlear nerve and overall auditory health is crucial. One of the most effective ways to prevent damage is by wearing appropriate hearing protection when exposed to loud noises. This can include earplugs or earmuffs, which help to reduce the intensity of sound reaching the cochlea.
Avoiding excessive noise exposure is also essential in preventing cochlear nerve lesions. This means being mindful of the noise levels in your environment and taking steps to minimize exposure whenever possible. For example, turning down the volume on personal listening devices or taking breaks from noisy activities can make a significant difference in protecting your hearing health.
Maintaining overall good health through a balanced diet and regular exercise can also contribute to the prevention of cochlear nerve lesions. A healthy lifestyle promotes optimal blood flow to the inner ear, ensuring that the cochlear nerve receives the necessary nutrients and oxygen for proper functioning.
Furthermore, individuals at risk should have regular check-ups with healthcare professionals to monitor their hearing status and address any concerns in a timely manner. These professionals can provide guidance on preventive measures specific to your individual circumstances and offer appropriate interventions if any signs of cochlear nerve damage are detected.
In conclusion, while cochlear nerve lesions can significantly impact an individual’s hearing, balance, and overall well-being, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of such damage. By identifying high-risk individuals and implementing preventive measures, such as wearing hearing protection and avoiding excessive noise exposure, we can strive to protect the delicate cochlear nerve. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are also important in ensuring early detection and effective management of any potential issues. By prioritizing our auditory health, we can enhance our quality of life and minimize the potential side effects associated with cochlear nerve lesions.